
When training clients, I look at 5 different components in their physical capabilities. Those components are strength, mobility, stability, aerobic efficiency and anerobic performance.
In this article, I will be sharing information on Zone 2 training in its importance and how to apply. Zone 2 training is in aerobic efficiency category. This does not mean that other 4 categories are inferior to zone 2 training, however, it is as much important component of fitness as the others.
Definition of zone 2 is your highest metabolic work that you can sustain while keeping the lactate level low (below 2 mmol/L). Biochemically, when exercising, our body use glucose, fatty acids, and oxygen and go through chemical process. This process is also known as mitochondrial respiration because majority of the chemical process to create energy is done within the mitochondria. While in zone 2, the fat utilization is generally higher than the glucose. As the lactate level increases, this shows that more glucose is being utilized as energy.

Mitochondria Respiration
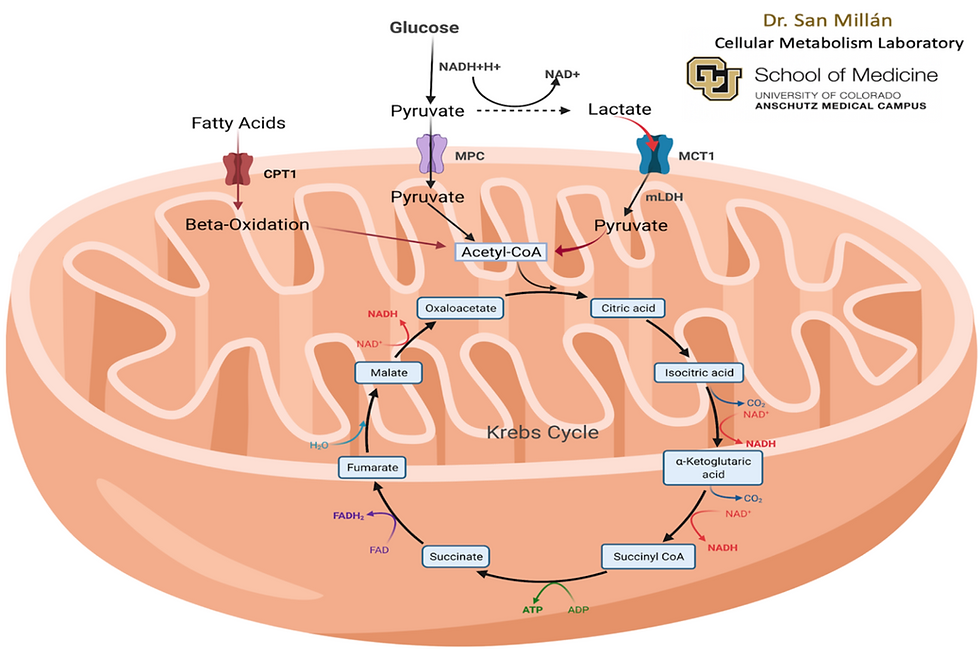
Mitochondria respiration refers to how mitochondria produce energy from fat and glucose for our daily performance. We have two energy sources that can be converted into energy, fatty acid, and glucose. Glucose will convert into two molecules called pyruvate and lactate.
Ideal primary energy source is fat. Stored fat or triglyceride can break up into 3 fatty acids and glycerol by the enzyme called hormone sensitive lipase (HSL). Fatty acid, then, with a help of the amino acid called carnitine, it enters mitochondria through the CPT1 transporter. Once the fatty acid enters the mitochondria, the process called Beta-Oxidation starts. This is the process where mitochondria further break down into acetyl-CoA. After the breakdown into acetyl-CoA then enters the last phase called Kreb cycle then to electron transport. Through this process mitochondria can generate 129 ATP from fatty acid.
Glucose has 2 pathways. First pathway is glucose breakdown to pyruvate through a process called glycolysis, then enter mitochondria convert into acetyl-CoA then enter Kreb cycle and electron transport like fatty acids. This process creates 32 ATP.
As we exercise, regardless of how fit you are, energy demand will increase. We do normally produce some amount of lactate, however, as energy demand increases, we create more lactate through glucose. Therefore, the second pathway for glucose is after broken down to pyruvate with decrease in cellular oxygen, then convert into lactate. If there’s enough MCT1 transporters in mitochondria, the lactate enters mitochondria then convert back to pyruvate. Pyruvate converts into acetyl-CoA and enters Kreb cycle and electron transport. In this process 32 ATP is created. You may see 2 ATP is created; however, studies have shown that even with lactate pathways can generate 32 ATP.
It is confusing but analogy I use is exchanging foreign currency. The body cannot use fat or glucose as energy just as it is. Therefore, mitochondria helps exchange them into currency called ATP so that body can use them. Exchange rate of fat is higher than the glucose but the process takes more steps then exchanging glucose into ATP.

Consequence of Training Without Understanding Mitochondria
Biggest issue that I see with people who are starting to train or coming back to training from injury or busy schedule, they focus more on how much calories they can burn off per session to make up for the lost time.
This can become counterproductive because, the body need to be trained or retrained to metabolize fatty acid as energy source, which requires us to train in Zone 2 for majority of the time to help recreate transporter in the mitochondria to bring in more fatty acid to convert them into energy. Training above your zone 2 will only allows you to use more glucose and not much of fat. When you have not been training, you will need to train the body at appropriate intensity.
Here is another problem. As mentioned earlier, when the physical exertion gets higher the body will produce lactate. People who has been trained at and above lactate threshold may able to utilize lactate as energy source. However, if you have never trained or have not been training in lactate threshold intensity level, chances are the mitochondria may not be able to use the lactate as energy source, which it will be spit out into a bloodstream. This can become a problem since lactate is acidic which can bring the blood pH level down to acidic as well.
Complication comes when people assume they had great workout and deserve wine, beer, energy drinks, coffee, sugary food. Along with lactate, these are all low in pH level which means acidic that can lower the blood pH level. Normally body will work to bring back the blood pH level through hydration, proper nutrition and sleep, however, when low blood pH level continues, the body can go into condition called metabolic acidosis where blood pH level gets below 7.35. Symptoms of metabolic acidosis can be fatigue, accelerate heartbeat (tachycardia), dizziness, loss of appetite, shortness of breath, headache and so on. Commonly, this condition is for those who have kidney issues but can’t rule out the possibility of training and dieting in a wrong manner, which may have potential to cause the similar the same condition.
By the way, training hard is not a bad thing. Training hard without understanding of purpose is a problem. Chasing after the calorie expenditure alone through exercising is the trend that may be causing more problem.
Zone 2 and Mitochondria Respiration
Biochemistry of mitochondria respiration is complicated to understand. But when understanding why we need to train to improve mitochondria respiration and how, will make better sense.
In healthy individual, from resting to lower intensity activities, such as walking in a grocery store, walking up and down the stairs, the body or mitochondria should be utilizing fatty acid as a primary energy source. While the exercise intensity is low the body does use glucose as energy source and produce lactate but in a minimal amount. This can vary from fitness level of the individual.
As the physical exertion increases to brisk walk, jog, run, bike, row, longer duration stair climbing, weightlifting, the body may demand more energy supply. For people who are fit, they may still utilize fat as primary energy source, however glucose demand and usage may increase. This level of physical exertion is called Zone 2 where primary energy source is fatty acid and sustaining lactate level low.

As the physical exertion increase even further, whether this could be intensity and/or duration, the body will demand glucose as energy source and produce more lactate. Eventually, there will be a point where the body need to utilize glucose only and this borderline is called lactate threshold.
Mitochondria Adaptation Through Zone 2 Training
When you train in Zone 2, you are training the mitochondria to utilize fatty acid as energy source more efficiently. What is happening is because the demand of fatty acid is increasing by training in Zone 2, the mitochondria need to have more transporters which allows to bring in more fatty acids. Eventually the body can utilize fatty acid more efficiently even at the higher exertion.
Another benefit with Zone 2 training is low accumulation of lactate. Those who have high stress or have metabolic issues, they may already have higher lactate level even at rest. This may mean that training above the Zone 2 may push the lactate into the bloodstream, which may cause more metabolic issues. However, if the training is in Zone 2, this may allow the person to exercise without accumulating too much lactate.

Ways to Find Your Zone 2
By now you may be thinking of how to find zone 2. There are several ways to find the zone 2 and can be separated into two categories, direct and indirect.
Direct way to find the zone 2 is through a device called metabolic cart. This is where you will be strapped with mask that is connected to the computer which reads the oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange while monitoring your heart rate and lactate. Heartrate will be monitored with heart rate monitor and lactate is through blood by finger plucking. Assessment can be done with treadmill, bike, rower, elliptical, swim and so on.
There are 2 indirect ways to find the zone 2, which will not be as accurate as metabolic cart but give you a rough idea. First is calculating 180 minus your age. So, if you are 50 years old the zone 2 heartrate will be 130bpm (beats per minutes). What I typically do is take this number and subtract 10 bpm to give a rough range. So, for someone who is 50 years old, the zone 2 range is from 120-130bpm. Reason why I subtract is because I want their body to be trained to use fat as energy source and minimize the possibility of going over the zone 2.
Second way is using RPE, which stands for Rate of Perceived Exertion. In other words, how are you feeling while you are exercising. Usually there is a number scale from 1-10 being used but what I typically tell my clients is keeping the intensity level that they feel that they are exercising but still can have a conversation. So, when I do have training session with client, I typically converse with client while they are exercising to see where they are in physical exertion. Of course, to have fun at the same time. This is convenient since you won’t need heartrate monitor to check for those who prefer not to wear any monitoring device, which I kind of understand.
Although indirect way is easy but it is not as accurate as direct way.
Conclusion
Zone 2 training is to train mitochondria to utilize fat as energy source. This is beneficial to both athletes and those who are wanting to get back into shape. By understanding Zone 2 and mitochondria respiration, training hard all the time is not the smart way to train and can cause more damage to the body despite the effort. 70-80% of the training should be done in Zone 2 and remainder can be pushed to Zone 3-5 depending on your training goal.
When looking at social media, you do see impressive workout clips where people are doing insane workout and have amazing physique. This doesn't mean that you should be doing it. First thing you should do is to learn about your body and start with what feels comfortable for you. Over doing exercise may cause elevation in stress hormone called cortisol and may hinder your progress although you are working hard and watching what you are eating.
When not sure, start with zone 2 method by monitoring your heart rate and RPE to know if you are pushing yourself too much too early.
Kota Shimada
Commentaires