
Basic of metabolism is how our body convert food into energy by metabolic process then utilize the energy based on our body’s need. In a way, it does sounds like calorie in/calorie out concept, however, it is more complicated than that. Because metabolism is publicly oversimplified, when it comes to fat or weight loss, many people are missing the entire picture. Of course, if you have been eating too much then you should cut down your food amount or calorie then you may see some results. But those who are struggling, there is chance that you are missing the entire picture of metabolism.
What is Metabolism?
Metabolism in simple term it is how our body process food into energy called ATP. Think of ATP as currency that the body use. By eating apple, broccoli, meat, fish, the body has no clue what to do with it. With metabolic process they convert food and convert them into fatty acids, glucose, and amino acids. Now the body knows how to use these three materials into ATP.
My favorite example is foreign currency exchange. When you travel to different country they use their own currency. So, when you travel to different country, you will need to exchange your money into their currency so that stores will know what to do with it. If you use credit card, currency will be exchanged automatically.
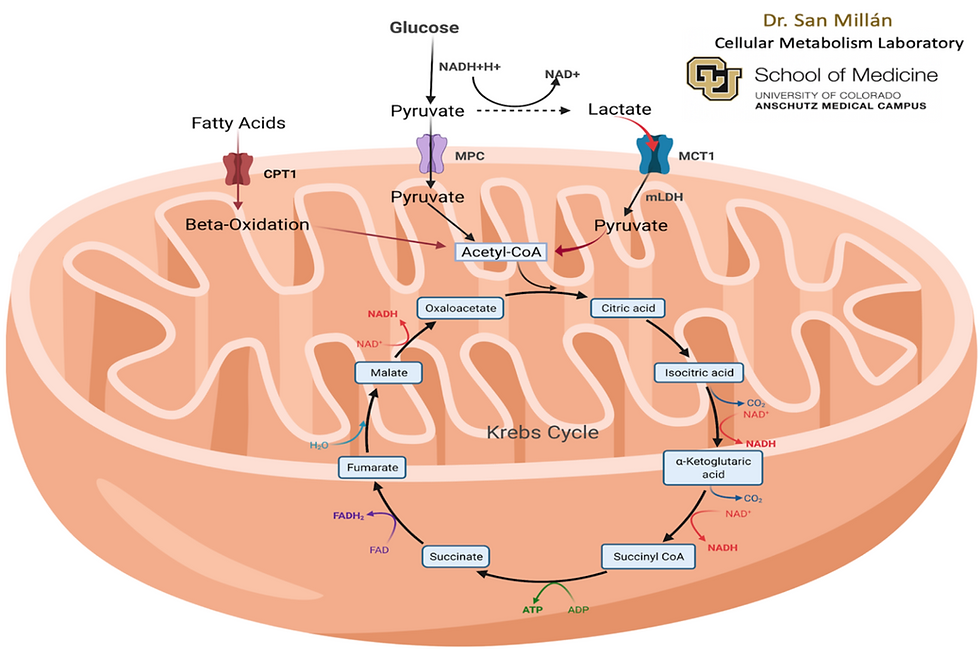
Mitochondria
Now the question comes, how our body convert fatty acids, glucose, and amino acids into ATP? Important organelle that our cell has that plays very important role in ATP creation is called mitochondria. Role of mitochondria is simple. Convert energy source such as fatty acids, glucose, amino acids into energy called ATP. Depending on stress factor and how our homeostasis is disrupted, selection of energy source change. What energy source to use is not selected by mitochondria. It is more of brain figuring out what energy source to maintain or adjust homeostasis according to the changes.
Homeostasis
What is homeostasis? Homeostasis is our body’s thermostats but not just for body temperature but for everything from blood sugar level, hormonal balance, blood pressure, and so on. Whenever you do blood testing or lipid profile with your doctor, they are looking at what parameter is your homeostasis having a difficulty of regulating. Let’s take blood sugar level. When you eat, your blood sugar level will increase. Depending on what you eat amount of blood sugar increase may vary. After a while, the body can bring down blood sugar level to the normal level around 86-100. If you have condition like insulin resistance or diabetes, this number may remain high for longer period.
Let’s put this into exercise. When you perform exercise homeostasis will be disrupted by body temperature increase, heart rate increase, oxygen and carbon dioxide ratio changes, blood sugar level drops, and so on. Because of this changes, mitochondria increase the rate of glucose, fatty acid, amino acid, into ATP according to the way the homeostasis is disrupted. This is a condition is known as increase in metabolic rate. Once the exercise is done, homeostasis will be regulated, and all the parameters will work towards returning to normal. Mitochondria will slow down their ATP production which it also means the body is decreasing in metabolic rate. Depending on type of exercise you have done and your condition, duration of recovery from exercise vary from person to person.
Fat Metabolism and Misconception
Fat metabolism is little bit complicated than just managing calories. Some of the key factors that we need to consider in fat metabolism are insulin to glucagon ratio, digestive absorption rate, stress, exercise intensity and duration, and your recovery, which includes nutrition and sleep.
Insulin and Glucagon
For the fat metabolism to happen, the insulin secretion needs to be as low as possible throughout the day. Why? Major role of insulin is to store. This is very important role because otherwise we cannot bring nutrients to our body. That is why condition such as insulin resistance and diabetes are a problem because transporter of nutrients is not able to be accepted by the cells. We also know that when insulin level is high our metabolism slows down, which makes sense because its role of storing energy and nutrients.
The counter hormone called glucagon only works while the insulin level is down. They are both secreted by pancreas but has complete opposite role. Glucagon is responsible for using energy, which also means when the glucagon level is higher than the insulin the metabolic rate increases.

Stress and Exercise
Another factors. Stress and exercise. Exercise is categorized as physical stress. Other stress categories are social and environmental stress. Majority of time the body can handle stress by work of homeostasis and metabolism. However, with poor diet and lack of sleep, the ability of the body to recover from those stress factors decline, which may lead to elevate in stress hormones (cortisol), elevate in insulin, elevate in blood pressures, elevate in resting heart rate, carbon dioxide output increases which may lead to increase in lactic acid even at rest. Because of poor diet and lack of sleep, cardiovascular health is down, immune system is lowered, along with insulin level and blood sugar level is high.
This is how the body become obese, increase in stiffness, susceptible to illnesses, digestive issues, allergic reaction to things you were not allergic to before, become insulin resistance, high blood pressure and so on.
Although exercise is important to keep us healthy and fit, people have tendency to train at the higher intensity too early in a hope that it will burn more fat. From physiological perspective high intensity exercise will only train your body to use glucose as energy source rather than fat. This is due to carbon dioxide and oxygen ratio, or we call it respiratory quotient (RQ). We know that as exercise intensity increases our body produce more carbon dioxide relative to the amount of oxygen intake. As the carbon dioxide production increases our body use glucose as energy source. Glucose has faster ATP production rate compared to fat. For exercises such as power lifting, high intensity interval training, boot camp, and so forth may require using glucose as energy source rather than fat.
If the fat metabolism is the goal, this may become an issue because not only the body is not conditioned to convert fatty acid into ATP but also the body may not be able to recover from the exercise which may lead to chronic fatigue, injury, disrupted sleep, and so forth. For the adaptation to the exercise to happen, the body need to recover from exercise, which will lead to adaptation. Physiologically, “calorie in, calorie out” approach is not an ideal for fat metabolism.
4 Key Factors for Fat Metabolism
Basic of metabolism is break down food, convert them to energy source (fatty acid, glucose, amino acids), then convert them into ATP.
For fat metabolism to become more efficient, few things need to happen. First, the insulin level needs to be suppressed as much as you can. Therefore, keeping meal frequency, including your snacking, to 2-3 times a day. This will help the insulin level to be low between meals and give your digestive system a time to break down food. Also, minimizing sugar intake become important. This will include fruits, cake, cookies, ice cream soft drinks, juice, alcohol and so on.
Second is improving your digestive system. Without adequate digestive absorption rate, efficiency of food to energy conversion rate will decrease. It is not just about getting fatty acids, glucose, and amino acids but also other micronutrients including vitamins and minerals. Micronutrients are critical in metabolic processing of fatty acids, glucose, and amino acids into ATP. Therefore, if you have digestive issues or a slower rate of digestive absorption rate, overall metabolic rate decreases. Consumption of dietary fiber is important but water, probiotics, prebiotics are also important. Pro and prebiotics can be found in fermented food such as yogurt, kimchi, natto, sauerkraut, kefir and so forth. If you are thinking of getting pre and probiotics through supplements, make sure to store it in the refrigerator.
Third is training the body to utilize fat through exercise. As mentioned earlier, you may be able to burn calories through high intensity training, however, majority of energy is coming from glucose and not from fatty acids. If you want to be efficient in fat metabolism, you should spend 80% of your training in lower intensity. Training protocol called zone 2 training will play very important role in training your body to utilize fatty acids into ATP. Zone 2 should be done at least 3-4 times per week for 20-40 minutes. You can attain this by using cardio equipment such as treadmill, bike, and rower, and using strength training but keeping the weight and tempo of the exercise low. Simple guideline is keeping the heartrate around 180 minus your age.

Fourth is recovery. Main focus of recovery is to bring the homeostasis back to norm. Without recovery, the body won't be able to adapt to the stress you have applied. Recovery and adaptation can be done with nutrition, relaxation routines and sleep. Consuming whole food rather than packaged or restaurant food help your body recover from daily stress better. If you are on special diet, such as vegan, carnivore, low carb, low fat, know what nutrients you may be lacking so you can use supplements to improve your recovery. Relaxation routine can be taking a warm bath, stretching, reading, and so on. Create some down time especially before bedtime so the brain can calm down and focus more on recovery while you are sleeping. Schedule your bedtime and waking time. We are creature of habit and the body do well by creating a pattern. Number of studies have shown that sleep less than 7 hours will disrupt your homeostasis and may impact your fat metabolism.
Summary
To lose fat, you need to train and condition the body to do so. Without proper understanding, you may be working hard but not able to see the results you are looking for. By understanding what contributes to improving in fat metabolism will help understand what you may be missing. Of course, as your condition improve you may need to adjust nutrition and training protocol, however, for initial starting point follow the 4 key factors shared in this article.
Kota Shimada
댓글