
We all carry some level of fat in our body. Lets say someone weighs 180lb and has bodyfat of 10%. Which means, this person has 18lb bodyfat. Because 1g of fat is equal to 9 kcal, 18lb (about 8200g) of fat is almost 74,000 kcal. Then, the question comes how do we maximize the use of this stored energy called fat? Where there's various ways of doing this, the most efficient way of training the body to utilize fat as primary energy source is by monitoring your heartrate and training in specific heartrate zone, which is also known as zone training.
To understand zone training you'll need to understand how our body creates energy. There are two major sources, glucose and fat. These two will be converted into energy by organelle called mitochondria which they live in our cells.
Learning Mitochondria Respiration
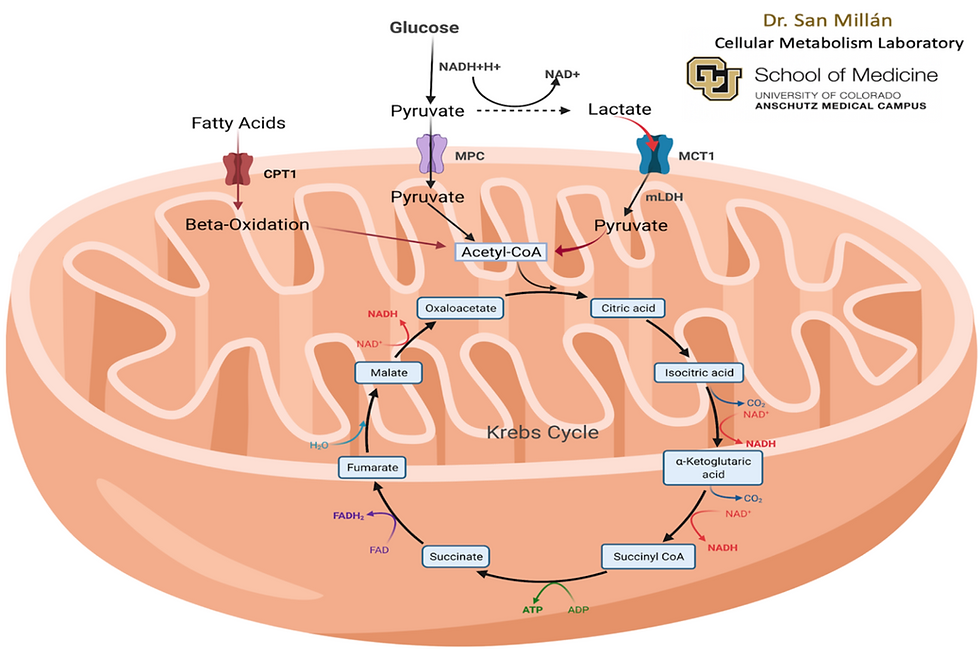
Mitochondria respiration refers to how mitochondria produce energy from fat and glucose for our daily performance. We have two energy sources that can be converted into energy, fatty acid, and glucose. Glucose will convert into two molecules called pyruvate and lactate.
Ideal primary energy source is fat. Stored fat or triglyceride can break up into 3 fatty acids and glycerol by the enzyme called hormone sensitive lipase (HSL). Fatty acid, then, with a help of the amino acid called carnitine, it enters mitochondria through the CPT1 transporter. Once the fatty acid enters the mitochondria, the process called Beta-Oxidation starts. This is the process where mitochondria further break down into acetyl-CoA. After the breakdown into acetyl-CoA then enters the last phase called Kreb cycle then to electron transport. Through this process mitochondria can generate 129 ATP from fatty acid.
Glucose has 2 pathways. First pathway is glucose breakdown to pyruvate through a process called glycolysis, then enter mitochondria convert into acetyl-CoA then enter Kreb cycle and electron transport like fatty acids. This process creates 32 ATP.
As we exercise, regardless of how fit you are, energy demand will increase. We do normally produce some amount of lactate, however, as energy demand increases, we create more lactate through glucose. Therefore, the second pathway for glucose is after broken down to pyruvate with decrease in cellular oxygen, then convert into lactate. If there’s enough MCT1 transporters in mitochondria, the lactate enters mitochondria then convert back to pyruvate. Pyruvate converts into acetyl-CoA and enters Kreb cycle and electron transport. In this process 32 ATP is created. You may see 2 ATP is created; however, studies have shown that even with lactate pathways can generate 32 ATP.
Physiology of mitochondria respiration is complex. To simplify, when the activity level is low or at rest, mitochondria will be converting fat as energy source. As the physical exertion increases body will start converting glucose as energy source because the conversion is faster than fat. Eventually, there will be a drop off point where body no longer can rely on fat energy source, then rely only on glucose. This cut off point is called lactate threshold. In Zone training this threshold point is where we divide zone 3 to zone 4.
Tracking Heartrate
Zone 2 is training is the most efficient training intensity level that we can burn as much calorie as we can while keeping the energy source, primarily, from fat. As we enter zone 3, although we may use higher calories compare to zone 2, however, ratio of fat to glucose usage is favoring towards glucose. Therefore, to train the body to utilize bodyfat more efficiently, it is ideal to train in zone 2.
Best way to monitor zone 2 is through heartrate. To find your zone 2, easiest way is to calculate 180-age. If you are 50 years old this will be 130bpm (beats per minute). However, trying to keep the heartrate exactly at one number is challenging so I usually give 10 bpm range, therefore, 130-140bpm is for 50 year old. This is just a guide and depending on individual these number will vary and especially as you train in Zone 2 for few months this number will change but it is a good place to start.
If you want to invest in testing you can take active metabolic testing. This is a cardio testing using any cardio equipment but with mask on that is connected to the computer. It is reading oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange while you are exercising to identify your zones.

There is also a device called Morpheus. Morpheus identifies your training intensity level based off of how well you have recovered. It will monitor your training and shows if you are in appropriate zone. Morpheus comes with heartrate strap and phone apps.
Sample Routine
Zone 2 training can be done with so many different ways. Here are some samples.
First is very simple. Using cardio equipment such as bike and treadmill for 30-60 minutes at heartrate zones that is appropriate for zone 2. Bike and treadmill is very useful since you can change the pace and resistance according to what you are feeling. One pointer while performing steady state type cardio for zone 2 training is target the lower range of your zone 2 heartrate. For example, if your heartrate range for zone 2 is 130-140bpm, then strive for 130bpm. Because as you go through 30-60 minutes, your heartrate will gradually increase.
Ex: Zone 2 Steady Cardio: 30-60 minutes
Second is intervals. Let's take bike or treadmill for example, you can raise your heartrate close to 140bpm for 2 minutes then bring the heartrate down close to 130bpm for 5 minutes and repeat this for 3-8 sets. You can also raise your heartrate by using medicine ball slam for 10-15 reps then get on the treadmill at 130bpm pace for 2 minutes than repeat for 4-5 sets.
EX: Zone 2 Intervals: (2 minutes at top of zone 2/ 5 minutes at bottom of zone 2) x 3

Third is circuit. You may choose 3 or more exercises and make it into a circuit based training. Because we do want to raise heartrate with each exercise, you may want to keep the repetitions relatively higher (15-20 reps). Keep in mind that if you are planning to add more weight to your exercise, you will be increasing your heartrate even further. As you exercise check your heartrate and adjust your repetitions and load. After each exercise, allow the heartrate to recover. This may take 20-60 seconds depending on your fitness level.
EX: Zone 2 Circuit for Legs
3 sets each with 2 minutes rest between each set
A1 15 Squats
A2 15ea Split Squats
A3 20 Straight Leg RDL
Summary
Zone 2 training is not just about burning as much as calories as possible. It is burning as much fat calories as possible. To do so, it is vital to control the intensity level of your exercise. While you are performing zone 2 training, you should feel "little challenge" but not exhausting. When you are doing zone 2 steady state cardio, you should be able to feel little challenge but able to have a conversation if you are training with your friends. Most important piece for zone 2 training is keep monitoring your heartrate. Ideally after each exercise and each set.
Kota Shimada
Comments