
When thinking about fat metabolism or utilizing fat as energy source, there are two key factors to consider.
First is insulin sensitivity. For those who are having difficulty losing fat, chances are they have condition called insulin resistance. Insulin is a hormone secreted by pancreas. Whenever we consume food, especially carbohydrate, pancreas produce insulin to transport the nutrients to the cells. Insulin resistance is when the cells in the body refuse to receive insulin. Because the cells are not wanting to receive package that insulin is trying to deliver to the cell will be sent to storage also known as fat.
Second key factor is mitochondria respiration. Mitochondria is an organelle that lives in our cell and their primary function is to convert glucose and fat into energy. Mitochondria respiration is how our mitochondria convert glucose and fat into energy and more you are trained mitochondria become more efficient energy production. Also, well planned training can help created more mitochondria which will become more efficient in energy production, hence the metabolism increase.
Improving Insulin Sensitivity
Depending on what condition you are currently in, where you will start to improve your insulin sensitivity is different. Two things must happen. Resolve your insulin resistance and building muscles.
If you already have insulin resistance you will need to solve this issue by monitoring your diet and regulate your sleep. From diet perspective, eating frequent meals or snacks, along with consuming food and drinks with high sugar must be avoided. I do realize that some advice you may receive is eat small frequent meal, like 4-6 meals a day. What is the point of doing that if you are already insulin resistant. It is important to understand that when we consume food, insulin will be secreted. For reversing insulin resistance, you will need to create down time for the insulin production by pancreas. Better plan would be start with 3 meals a day. Meal will include snack, protein shake, latte, alcohol, meal and so on. Anything that has calorie consider that to be a meal.

Strength training on weekly basis will help improve your insulin sensitivity. More muscle you build, more muscle fiber you will have. Which also means that insulin can be received at more location. Some of the great exercises you can work on are squats, bench press, rows, lunges, and deadlift. Of course, some of the exercises may require you to learn the proper technique but in the process of learning you will be building muscles to so give them a try. Also, don't be afraid of lifting heavy. You may want to start off light but you should strive for lifting heavier weight.
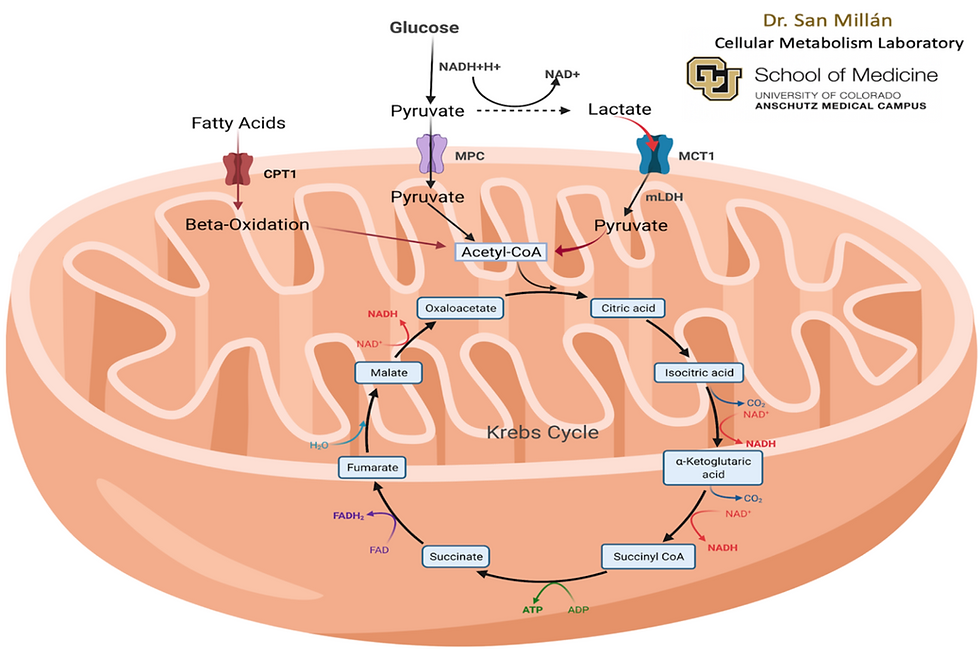
Improving Mitochondria Respiration
Mitochondria respiration refers to how mitochondria produce energy from fat and glucose for our daily performance. We have two energy sources that can be converted into energy, fatty acid, and glucose. Glucose will convert into two molecules called pyruvate and lactate.
Ideal primary energy source is fat. Stored fat or triglyceride can break up into 3 fatty acids and glycerol by the enzyme called hormone sensitive lipase (HSL). Fatty acid, then, with a help of the amino acid called carnitine, it enters mitochondria through the CPT1 transporter. Once the fatty acid enters the mitochondria, the process called Beta-Oxidation starts. This is the process where mitochondria further break down into acetyl-CoA. After the breakdown into acetyl-CoA then enters the last phase called Kreb cycle then to electron transport. Through this process mitochondria can generate 129 ATP from fatty acid.
Glucose has 2 pathways. First pathway is glucose breakdown to pyruvate through a process called glycolysis, then enter mitochondria convert into acetyl-CoA then enter Kreb cycle and electron transport like fatty acids. This process creates 32 ATP.
As we exercise, regardless of how fit you are, energy demand will increase. We do normally produce some amount of lactate, however, as energy demand increases, we create more lactate through glucose. Therefore, the second pathway for glucose is after broken down to pyruvate with decrease in cellular oxygen, then convert into lactate. If there’s enough MCT1 transporters in mitochondria, the lactate enters mitochondria then convert back to pyruvate. Pyruvate converts into acetyl-CoA and enters Kreb cycle and electron transport. In this process 32 ATP is created. You may see 2 ATP is created; however, studies have shown that even with lactate pathways can generate 32 ATP.
It is confusing but analogy I use is exchanging foreign currency. The body cannot use fat or glucose as energy just as it is. Therefore, mitochondria help exchange them into currency called ATP so that body can use them. Exchange rate of fat is higher than the glucose, but the process takes more steps than exchanging glucose into ATP.

Training in Zone 2
In healthy individual, from resting to lower intensity activities, such as walking in a grocery store, walking up and down the stairs, the body or mitochondria should be utilizing fatty acid as a primary energy source. While the exercise intensity is low the body does use glucose as energy source and produce lactate but in a minimal amount. This can vary from fitness level of the individual.
As the physical exertion increases to brisk walk, jog, run, bike, row, longer duration stair climbing, weightlifting, the body may demand more energy supply. For people who are fit, they may still utilize fat as primary energy source, however glucose demand and usage may increase. This level of physical exertion is called Zone 2 where primary energy source is fatty acid and sustaining lactate level low.
Type of exercises that you can use for Zone 2 training is limitless. This can be walk, bike, lift, or even combination of these. Only thing you'll need to be worrying about is to maintain the intensity level in Zone 2. Best way to monitor this is through heartrate. To find your Zone 2 easiest way is to calculate 180-age. If you are 50 years old this will be 130bpm (beats per minute). However, trying to keep the heartrate exactly at one number is challenging so I usually give 10 bpm range, therefore, 130-140bpm is for 50 year old.
Now this is just a guide and depending on individual these number will vary and especially as you train in Zone 2 for few months this number will change but it is a good place to start. If you want to invest in testing you can take active metabolic testing. This is a cardio testing using any cardio equipment but with mask on that is connected to the computer. It is reading oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange while you are exercising to identify your zones.
There is also a device called Morpheus. Morpheus identifies your training intensity level based off of how well you have recovered. It will monitor your training and shows if you are in appropriate zone. Morpheus comes with heartrate strap and phone apps.
Sample Weekly Schedule to Improve Fat Metabolism
If you already have a weekly training schedule don't change anything unless it is not working for you. But for those who are looking for sample training schedule you can use the below as a guide.
Monday Leg Strength and Zone 2
Tuesday Upper Body Strength and Zone 2
Wednesday Rest
Thursday Leg Strength and Zone 2
Friday Zone 2
Saturday Upper Body Strength and Zone 2
Sunday Rest
To keep it simple, I've separated the strength training in 2 phases leg and upper body. This can be rearrange for your convenience. For proper muscle recovery stay within 2-4 strength training sessions in a week.
Zone 2 here is mainly cardio exercises. This can be walk or bike but keep track of your heartrate. Intensity level is moderate so you can recover faster than strength training. Also it does take some time for body to efficiently utilize fat so frequency should be 4-6 days per week. Duration of strength training should be 30-60 minutes and Zone 2 training should be 20-45 minutes.
When planning for fat loss or improve your body's fat utilization, keep in mind the 2 key factors. This goes for both diet and exercise. Have a purpose in mind. It is not just about calorie in and calorie out. It is managing your insulin and training your body to use fat as a fuel.
Kota Shimada
Comments